There are various news reports today that the North Korea nuclear weapon test on Sunday triggered landslides in the local terrain. This is based on an initial analysis of Planet Labs imagery by three analysts from 38 North, which is dedicated to analysis of events in North Korea. Their report says:
Commercial satellite imagery from Planet, obtained the day after North Korea conducted its largest test to date (currently estimated in the 100+ kiloton range), appears to show numerous landslides throughout the Punggye-ri Nuclear Test Site and beyond
And they have produced this image:-
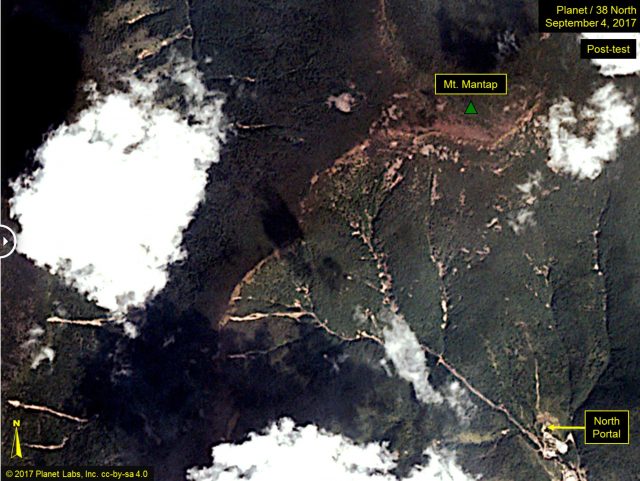

38 North and Planet Labs imagery of the site of the North Korea nuclear weapons test. Image collected after the test showing landslides triggered by the underground blast.
.
This appears to be interpreted in some quarters to indicate that the weapon was particularly large. For example, Newser has the headline:
This is a Planet Labs image from 6th September (i.e. today) showing the area of Mount Mantap affected by the underground nuclear weapons test:-

Planet Labs image of 6th September 2017 showing the area affected by the North Korea nuclear weapon test
.
This is the same area on a Planet Labs image dated 26th August, definitely collected before the most recent weapons test:
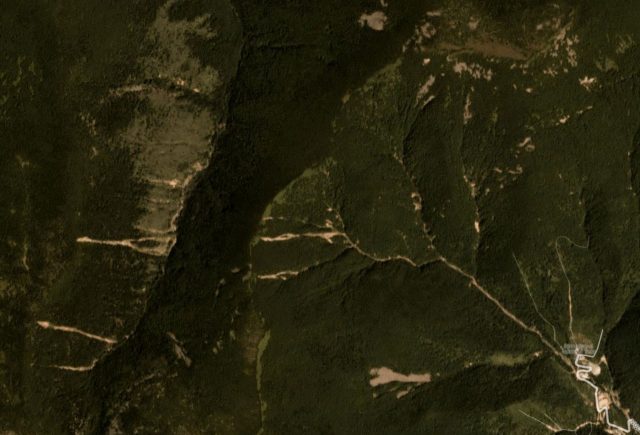

Planet Labs image of the area affected by the North Korea nuclear weapon test. Image collected on 26th August 2017, prior to the test
There are undoubtedly some new landslides in the post-test image, although most of the larger ones in the imagery were pre-existing. The new landslides appear to be mostly small, and they are focused close to the channel, perhaps where there is either accumulated debris or steeper slopes due to incision. There are a few larger events in the gully systems. It is not the case, as far as I can see, that there is very extensive landsliding in the area affected by the nuclear weapons test – certainly not on the scale that we see from major earthquakes in mountainous areas.
That underground nuclear weapons tests trigger landslides in local mountain areas is not new, and nor is it surprising. The explosion induces ground shaking that is similar in some ways to an earthquake, although the nature of the shaking itself is quite different. In fact, the North Korean landslides are very localised and small compared with some other examples. In a book chapter that is partly online, the Russian landslide scientist V.V. Adushkin describes rock avalanches triggered by eight different underground nuclear weapons tests at the Soviet Novaya Zemlia test site during the subterranean weapon testing programme there. Two of these were enormous – the largest had a volume of 80 million m³, whilst another had a volume of 5 million m³. This is clearly very much larger than the landslides in North Korea.